Electric Vehicle Terminology

Confused about the terminology surrounding electric vehicles? We've covered the basics to get you up to speed.
On this page:
A BREAKDOWN
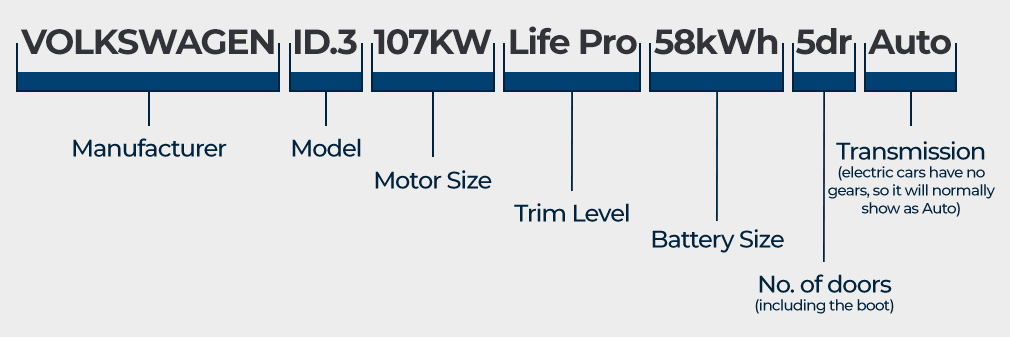
Above is an example of an electric car description. The descriptions will generally start with the manufacturer, then list the model followed by what is known as the 'derivative' or 'variant'.
The derivative normally details the engine size, turbo details (which may also denote the fuel type), trim level (the set specification the car comes with), number of doors and transmission type.
For electric cars, the details remain largely the same, however there is now the inclusion of the battery and motor details. The motor (which propels the car) size is listed as a numerical figure in kilowatt units. Generally, this will be the first of two listings referring to kilowatts.
The battery size (which stores the energy and determines the vehicle's range) is also listed as a numerical figure however this will be listed in kilowatt-hours, and is normally shown after the motor size.
Trim level details are usually found between these figures, whilst the number of doors (including the boot lid) and transmission will end the description. The latter will normally be shown as 'Auto' or 'Automatic' for electric models, which have no traditional gears except for Drive, Reverse, Neutral and Park.
TERMINOLOGY - AN INDEX
Below is an index of keywords that you will usually hear when talking about leasing an electric vehicle.
|
800V |
|
800V is one of the most powerful types of charging that can add as much as 60 miles of power in just 5 minutes. |
|
AC/DC |
|
This references both Alternating and Direct Currents. See our definitions of AC and DC below for specific definitions of these types of electricity flows. |
|
AC |
|
An Alternating Current is a type of electricity flow that can charge electric vehicles at slower speeds. You’ll find AC on home charging wall boxes. |
|
Battery |
|
The component that stores the electricity that powers the motor. |
|
BEV |
|
Battery Electric Vehicles are another way of saying fully electric vehicles. These are cars that are powered solely by a battery and do not require petrol or diesel, as hybrid cars do. |
|
CCS |
|
CCS stands for Combined Charging System and is the standard for charging electric vehicles in the EU. Its layout consists of two DC pins that sit below the standard Type 2 connector plug. |
|
CHAdeMO |
|
This is the name of a large, round four-pin charging plug that is only used at rapid charging stations. ChDeMo plugs are capable of Vehicle to Grid (V2G) charging but are less powerful than CSS. Many East Asian manufacturers like Nissan and Toyota use these chargers. |
|
Charging Point |
|
The name for the location where you fill up your car with electricity. |
|
DC |
|
Direct Current is a type of electricity flow that can charge electric vehicles at faster speeds. Electric cars have to convert AC power from the mains into DC before they can store it in the battery and this process takes extra time. DC charging stations cut out this process by providing DC power straight to the battery. |
|
Fast Charging |
|
A type of charging station, typically capable of charging at higher speeds. |
|
FCEV |
|
A Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle is another name for a hydrogen car. They run on hydrogen instead of electricity and typically have ranges that exceed 300 miles. |
|
HEV |
|
A Hybrid Electric Vehicle is a petrol or diesel car that also has a small electric motor and battery. HEVs don't have a plug, instead, they get their power from the engine or through regenerative braking. |
|
Hybrid |
|
Hybrid cars come in many shapes and sizes. They combine either a petrol or diesel engine with an electric battery and motor to create a vehicle that emits less carbon dioxide. Plug-in hybrids contain a bigger battery and can be recharged. |
|
ICE |
|
An Internal Combustion Engine is a traditional engine that typically runs on either petrol or diesel. In 2030 there will be a ban on the sale of new ICE vehicles in the UK. |
|
Kilowatt (kW) |
|
1,000 watts. This unit of measurement is typically used when referring to electric vehicles. |
|
Kilowatt-Hour (kWh) |
|
A kilowatt-hour is a unit of measurement for calculating how much electricity you've used and how large a battery is. It is the mpg equivalent for electric cars. |
|
Li-ion |
|
Lithium-ion is the type of battery that is used in electric cars, phones and laptops. |
|
Manufacturer |
|
The company that makes the vehicle. |
|
MHEV / MHD |
|
A Mild Hybrid Electric Vehicle can be either petrol or diesel and will usually come with a 48-volt system that includes an extra battery. This helps assist the engine as well as power onboard tech. MHEV batteries don’t have enough power to run the car on electrical energy alone. |
|
Model |
|
The vehicle designation. |
|
Motor |
|
The component that propels the vehicle. |
|
PHEV |
|
A Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle is a petrol or diesel car that also has an electric battery that can be plugged in and charged up. Unlike a MHEV, a PHEV can run on electric power alone before switching to petrol/diesel when the battery runs flat. |
|
Range |
|
The distance a vehicle will travel on a single charge from 100% capacity. |
|
Range Anxiety |
|
The fear of running out of charge before reaching a charging point. |
|
Rapid Charging |
|
A type of charging station, typically capable of charging at higher speeds. |
|
Regenerative Braking |
|
A system that uses energy generated from braking to add charge back into the battery. Also known as brake recuperation. |
|
Transmission |
|
Typically manual or auto/semi-auto. For electric and hybrid models, this is normally limited to auto. |
|
Trim, Variant or Spec[ification] |
|
The component that defines the standard equipment. |
|
Type 1 Cable |
|
A circular charging plug that has 5 pins and a clip. This type of connector is much more common in the US. |
|
Type 2 Cable |
|
A charging plug that has 7 pins and a flat edge. This type of charger is becoming the standard on most new electric vehicles. |
|
ULEZ |
|
The Ultra Low Emission Zone is an area in London where high polluting vehicles get charged a daily rate if they drive within its borders. |
|
Wall Box |
|
A unit installed to provide an accessible charging point. |
|
WLTP |
|
The Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicle Test Procedure is used to measure the fuel consumption and CO2 emissions from passenger cars and vans. The testing is conducted in a laboratory across different temperatures to reflect real-world driving conditions. In 2018, WLTP became mandatory for measuring the C02 emissions and EV ranges on all new cars in the EU. |
CHARGING CONNECTORS

CCS stands for Combined Charging System and is the most common connector for EVs across Europe. This connector will be available to use at DC rapid or ultra rapid charging stations.
As pictured above, the CCS connector consists of two DC pins that sit below a standard Type 2 connector ‘plug’ that we’ll look at below.

CHAdeMO connectors are usually only seen on vehicles that have a manufacturer from East Asia, such as Nissan, Mitsubishi or Kia.
As pictured above, the CHAdeMO ‘plug’ is circular with 4 round pins. This connector will be available to use when charging at a DC rapid or ultra rapid charging station.

Type 2 is the most common connector for AC charging. You’ll often need to bring your own Type 2 charging cable with you when you plug in at an AC charging point. Just like CCS, Type 2 is becoming the standard across new electric vehicles.
As pictured above, a Type 2 connector is circular with 7 pins and a flat edge. You’re most likely to find Type 2 connectors on street posts or on your own home charger.
KILOWHAT?
Kilowatts are a fundamental part of electric vehicle terminology. When reading about anything EV related you'll be sure to come across this word - so what does it mean?
kWh
kWh stands for kilowatt-hour and is a measurement of electricity. Knowing what a kWh is will help you understand how much energy you are using.
You’ll see kilowatt-hours used when looking at a car’s battery size. The bigger the battery in kWh, the more electricity you’ll be able to fit into it.
For example, a Kia EV6 with a 77.4kWh battery can store a maximum of 77.4 kilowatt-hours of electricity. More simply, a battery this size would be able to run a 1kW appliance like a kettle for 77.4 hours.
kW
Another measurement you’ll come across is a kW. A kW, as you may have guessed, stands for kilowatt and is equal to 1,000 watts.
Kilowatts are often used to measure the power created by a motor or engine, which you’ll see in the description of an electric car derivative. A kW can also be used to describe how quickly a charging point can fill up a battery.
For example, the power outputs of chargers can be anything from 3.6kW up to 350kW. The higher the kW, the quicker the charging point can move electricity into your car. However, not all cars will have the compatibility to charge at those higher rates.

